A Residency Declaration Form, often a critical document, holds the key to establishing one’s official residential status. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into its meaning, explore various types, provide practical examples, share insights on creating a foolproof form, and offer valuable tips. Whether you’re navigating changes in residency, applying for benefits, or addressing legal matters, understanding Residency Declaration Forms is your essential compass to ensure accurate, legally compliant declarations.
What is a Residency Declaration Form? – Definition
A Residency Declaration Form is a legal document used to declare one’s official place of residence or domicile. It is typically used for various purposes, such as establishing eligibility for in-state tuition, voting, tax purposes, or accessing government benefits. These printable form requires individuals to provide detailed information about their residency, including their current address, length of residence, and sometimes supporting documentation. By completing and submitting this form, individuals affirm their residency status and comply with legal requirements in a given jurisdiction.
What is the Meaning of the Residency Declaration Form?
The meaning of a Residency Declaration Form lies in its role as a legal document used to officially declare one’s place of residence or domicile. It serves as a formal statement confirming an individual’s residency status for various purposes, such as determining eligibility for in-state tuition, voting rights, taxation, and access to government benefits. This document holds significance in legal and administrative contexts, helping establish an individual’s ties to a specific jurisdiction and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations related to residency.
What is the Best Sample Residency Declaration Form?
The best sample Residency Declaration Form can vary depending on the specific purpose and jurisdiction it’s intended for. However, here’s a detailed outline of what a comprehensive Residency Declaration Form should typically include:
Section 1: Personal Information
- Full Name: The individual’s legal name, including first, middle, and last names.
- Date of Birth: The individual’s date of birth for identification purposes.
- Social Security Number or National Identification Number (if applicable): Certain jurisdictions may require the inclusion of a unique identifier.
- Contact Information: The individual’s current contact details, including their address, phone number, and email address.
Section 2: Current Residency Information
- Current Address: The address where the individual currently resides.
- Length of Time at Current Address: The duration of time the individual has lived at their current address.
- Previous Address (if applicable): If the individual recently moved, they may need to provide their previous address.
- Reason for Change of Address (if applicable): An explanation of why the individual changed their address, if applicable.
Section 3: Residency Declaration
- Statement of Residency Declaration: A straightforward statement where the individual declares their current place of residence. For example: “I hereby declare that my current residence is [current address], and I understand the legal implications of this declaration.”
Section 4: Legal Considerations
- Compliance Statement: A statement indicating that the individual understands and agrees to comply with all relevant local, state, and federal laws and regulations regarding residency within the jurisdiction.
- Penalty Statement: A statement outlining potential penalties, legal consequences, or liabilities for providing false or fraudulent information on the form. This serves as a deterrent against providing inaccurate information.
Section 5: Supporting Documentation
- List of Required Documents: If the jurisdiction requires supporting documents as proof of residency (e.g., utility bills, lease agreements, government-issued identification), list them here.
- Instructions: Provide clear, step-by-step instructions on how to submit or attach the necessary supporting documents.
Section 6: Signature and Date
- Signature: A designated space for the individual to physically sign the form, indicating their agreement with the declaration and understanding of its legal implications.
- Date: A space for the individual to enter the date they signed the form.
Section 7: Notary Section (if required)
- Notary Public: In cases where notarization is necessary, include a section for a notary public to acknowledge the individual’s signature. This section typically includes space for the notary’s signature, stamp, and the date of notarization.
Section 8: Contact Information
- Contact details for inquiries or questions related to the form, such as a phone number, email address, or physical address where the form should be submitted.
Section 9: Important Notes
- Additional important information, such as deadlines for form submission, the specific office or department to which the form should be sent, and any special instructions or considerations.
Section 10: Certification
Please note that the specific requirements and format of a Residency Declaration Form can vary based on local laws and regulations. It’s advisable to consult with the relevant authorities or legal experts to ensure that the fillable form you use complies with the specific requirements of your jurisdiction.
FREE 40+ Residency Declaration Forms in PDF
1. Residency Declaration Form
2. Residency Declaration for Tuition

3. Sample Residency Declaration Form
4. Declaration of Residency Form

5. Residency Declaration Form for College

6. School Declaration of Residency Form

7. Declaration of Current Residency Form
8. Revenue Department Declaration of Residency Form

9. Student Residency Declaration Form
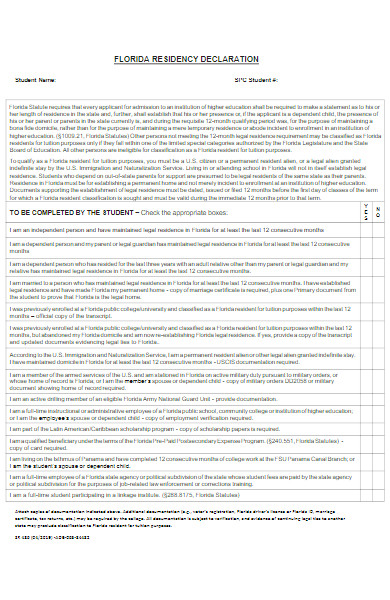
10. Request for Residency Declaration Form

11. Filmworks Declaration of Residency Form

12. Driver Residency Declaration Form

13. Declaration of Domicile Form

14. Medical Residency Declaration Form

15. Film Office Declaration of Residency Form

16. Tax Residency Declaration Form

17. Illegal Residency Declaration Form
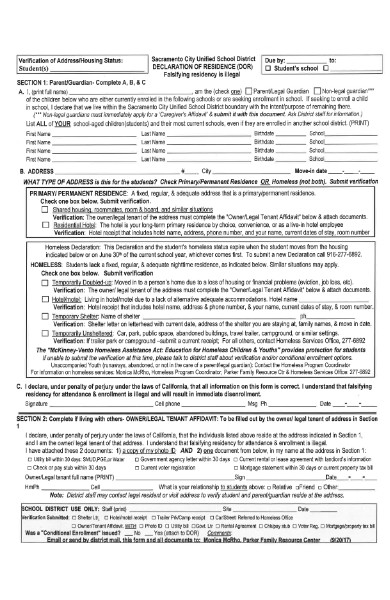
18. Simple Residency Declaration Form

19. Declaration of Residency Form for Non-Residents

20. Foreign Tax Residence Declaration Form

21. Producer Residency Declaration Form

22. Parent Guardian Declaration of Residency Form

23. Declaration of Residency Form Example

24. Tax Residency Declaration Form in PDF

25. Declaration of Student Residency Form

26. Residency Declaration for Tuition Purposes Form

27. Declaration of Tax Residence for Individuals Form
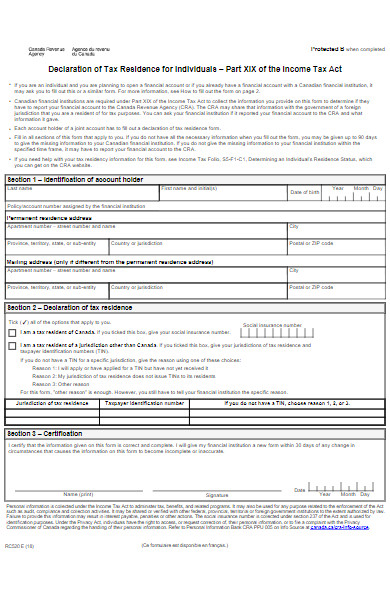
28. Students Grades Residential Declaration Form

29. Health Trust Declaration of Residency Form

30. Basic Residency Declaration Form

31. Film Declaration of Residency Form

32. Declaration of Tax Residence for Individuals

33. Declaration Form for Residency Applicants
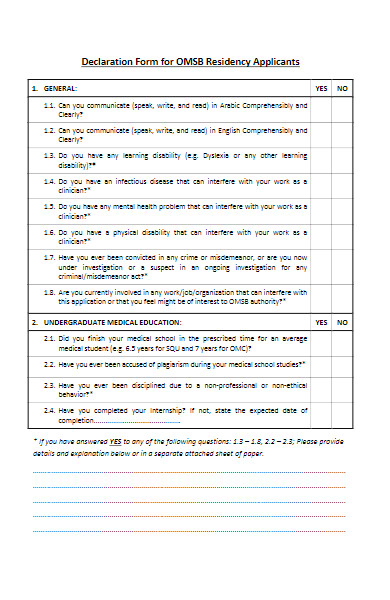
34. Standard Declaration of Residency Form

35. Individual Tax Residency Self-Certification Form

36. Tax Residency Self Certification Declaration Form
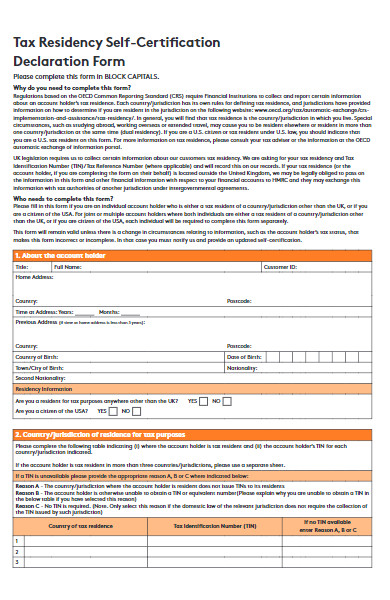
37. Residency Declaration Form in PDF

38. Individual Residency Declaration Form

39. Texas State Residency Declaration Form

40. Declaration of Residency Status Form
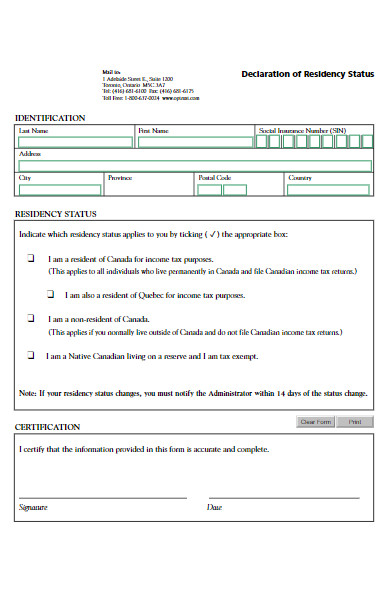
41. Residency Declaration Form for School

Why do I need a Residency Declaration Form?
You may need a Residency Declaration Form for several important reasons:
- Proof of Residency: Residency Declaration Forms are often used to establish and document your official place of residence. This can be essential for various legal and administrative purposes.
- Eligibility Determination: Many institutions, such as schools, colleges, and universities, use Residency Declaration Forms to determine eligibility for in-state tuition rates. Having accurate residency documentation can significantly impact educational costs.
- Voting Rights: Residency declaration may be required to register to vote in local, state, or national elections. It ensures that you are eligible to participate in the democratic process.
- Tax Purposes: Residency status can affect your tax obligations, including income tax, property tax, and eligibility for tax credits or deductions. Accurate residency documentation is crucial for tax compliance.
- Government Benefits: Some government benefits and assistance programs are contingent on residency status. Proper documentation helps you access the benefits you may be entitled to.
- Legal Matters: In certain legal proceedings, residency can be a significant factor. Residency Declaration Forms can provide proof of your residence in such cases.
- Employment Verification: Employers may request residency documentation for employment verification or to determine eligibility for certain benefits or incentives.
- Access to Services: Residency documentation may be necessary to access specific services, such as healthcare, public transportation, or community programs.
- Loan and Mortgage Applications: When applying for loans or mortgages, your residency status can affect interest rates and terms. Lenders may request residency documentation.
- Immigration and Visa Processes: Residency status is vital in immigration and visa applications. Accurate documentation can impact your immigration status.
- Legal Obligations: In some cases, you may have a legal obligation to declare your current place of residence, such as during the census or as part of a legal proceeding.
Overall, a Residency Declaration Form helps you officially establish and declare your place of residence, ensuring that you comply with relevant laws, regulations, and requirements while accessing benefits and services that align with your residency status.
How do I fill out a Residency Declaration Form correctly?
To fill out a Residency Declaration Form correctly, follow these steps:
- Read the Instructions: Start by carefully reading any instructions provided with the form. Ensure you understand the purpose of the form and any specific requirements or documents you need to attach.
- Personal Information: Provide your full legal name, date of birth, and any identification numbers (such as a social security number) as required.
- Contact Information: Include your current address, phone number, and email address. If you’ve recently moved, provide your previous address and indicate the reason for the change.
- Residency Declaration: In the designated section, clearly declare your current place of residence. Be concise and accurate in your statement.
- Legal Considerations: Acknowledge your understanding of and agreement to comply with all relevant laws and regulations related to residency in the jurisdiction. Read and consider any penalty statements carefully.
- Supporting Documentation: If the form requires supporting documents as proof of residency, gather these documents and attach them as instructed. Common examples include utility bills, lease agreements, or government-issued identification.
- Signature and Date: Sign and date the form in the designated spaces. Your signature indicates your agreement with the declaration and your understanding of its legal implications.
- Witness or Notary (if required): If the form requires a witness or notary, ensure that this step is completed according to the form’s instructions. A notary may be necessary for legal documents.
- Review the Form: Before submission, review the entire form for accuracy and completeness. Ensure that all required fields are filled out, documents are attached if needed, and your signature is in place.
- Submit the Form: Follow the instructions for submitting the form. This may involve mailing it to a specific address, submitting it in person at an office or institution, or using an online submission portal if available.
- Keep Copies: Make copies of the completed form and any supporting documents for your records. These copies can be essential for reference in the future.
- Follow Up: If you’re submitting the form for a specific purpose, such as in-state tuition or voting registration, follow up to confirm that your application has been processed and your residency status updated as necessary.
Remember that the specific requirements and format of Residency Declaration Forms can vary based on jurisdiction and purpose. It’s crucial to carefully follow the instructions provided with the form to ensure you complete it correctly and comply with local regulations. If you have any doubts or questions, consider seeking guidance from the relevant authority or legal counsel. You may also be interested to browse through our other Affidavit of Residency Forms.
What documents should I provide with my Residency Declaration Form?
The documents you should provide with your Residency Declaration Form can vary depending on the specific requirements of the jurisdiction and the purpose of the declaration. Here are some common types of documents that may be requested or required as supporting evidence for your residency declaration:
- Proof of Address:
- Utility Bills: Recent utility bills (e.g., electricity, water, gas, internet) in your name and showing your current address.
- Lease or Rental Agreement: A copy of your lease or rental agreement that includes your name and current address.
- Mortgage Statement: If you own a property, a mortgage statement with your name and property address.
- Government-issued Identification:
- Driver’s License: A valid driver’s license issued by the state or jurisdiction in which you are declaring residency.
- State ID Card: A state-issued identification card with your current address.
- Passport: If applicable, a copy of your passport with a visa or immigration status indicating residency.
- Voter Registration:
- Voter Registration Card: If you are using the Residency Declaration Form for voting purposes, provide your voter registration card.
- Tax Documents:
- State Income Tax Return: A copy of your state income tax return, if applicable, indicating your state of residence.
- Property Tax Statement: A property tax statement or assessment indicating your property’s location and your ownership.
- Financial Records:
- Bank Statements: Recent bank statements with your current address.
- Pay Stubs: Pay stubs from a local employer that show your place of work and residence.
- School Records (if applicable):
- School Enrollment or Registration: If you are using the form for educational purposes, such as in-state tuition, provide school enrollment or registration documents.
- Affidavits (if required):
- Affidavit of Residency: In some cases, you may need an affidavit of residency from a landlord, parent, or legal guardian.
- Other Supporting Documents:
- Any additional documents that demonstrate your ties to the jurisdiction, such as vehicle registration, insurance policies, or membership records for local organizations.
It’s important to carefully review the Residency Declaration Form and its instructions to determine which specific documents are required. Some forms may require notarization or the signature of a witness, so be sure to follow the form’s guidelines accurately.
If you have any doubts or questions about the required documents, consider reaching out to the relevant authority or institution for clarification or seek legal advice to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Are Residency Declaration Forms the same for all states?
Residency Declaration Forms are not the same for all states or jurisdictions. They can vary significantly in terms of format, content, and specific requirements. Each state or jurisdiction may have its own Residency Declaration Form tailored to its laws, regulations, and administrative needs.
The variations in Residency Declaration Forms can include:
- Purpose: The purpose for which you are declaring residency can impact the content of the form. For example, forms for in-state tuition eligibility may differ from those used for voter registration.
- Required Documentation: Different states may require specific supporting documents to establish residency. These requirements can vary widely.
- Legal Language: The language and legal terminology used in the forms can differ based on state-specific laws and regulations.
- Notarization: Some states may require notarization of the form, while others may not.
- Form Design: The overall design and layout of the form can vary, including the placement of sections and fields.
Given these variations, it’s essential to use the Residency Declaration Form specific to the state or jurisdiction in which you are declaring residency. Using the wrong form can result in delays or complications in your application or declaration process.
If you are unsure which form to use or if you have questions about the specific requirements in your state, it’s advisable to contact the relevant government agency, educational institution, or legal counsel for guidance. They can provide you with the correct form and ensure that you complete it accurately to meet your residency needs. You should also take a look at our residence questionnaire form.
Do I need a lawyer to help me with my Residency Declaration Form?
Whether or not you need a lawyer to help you with your Residency Declaration Form depends on several factors, including the complexity of your situation and the specific requirements of your jurisdiction. Here are some considerations to help you decide:
- Complexity of the Form: If the Residency Declaration Form is straightforward, and you have a clear understanding of your residency status and the required documents, you may not need a lawyer’s assistance.
- Legal Advice: If you have questions about the legal implications of declaring residency or if your situation is more complex, consulting with a lawyer can provide valuable legal advice. This is especially important if the declaration involves significant legal consequences.
- Notarization: Some forms require notarization, which involves a notary public verifying your identity and the authenticity of your signature. While you can typically complete this step without a lawyer, a notary public’s services may be required.
- Supporting Documents: If gathering the necessary supporting documents is challenging or if you’re unsure which documents to provide, a lawyer can help ensure you submit the correct paperwork.
- Special Circumstances: If you have unique circumstances, such as dual residency in different states or complicated legal issues, legal guidance can be invaluable in navigating the process.
- Disputes or Legal Challenges: If you anticipate disputes or legal challenges related to your residency declaration, having a lawyer represent your interests can be crucial.
- Education or Employment: If you are using the declaration for purposes such as in-state tuition or employment eligibility, it’s essential to comply with the specific requirements of the educational institution or employer. A lawyer can help you understand these requirements.
- Immigration Status: If your residency declaration is related to immigration or visa matters, legal counsel is highly recommended due to the complexity of immigration law.
In many cases, individuals can successfully complete Residency Declaration Forms on their own, especially when the requirements are clear and straightforward. However, if you have any doubts, questions, or unique circumstances, it’s wise to consult with a lawyer who specializes in residency or immigration law. They can provide you with legal advice, ensure compliance with relevant laws, and help you navigate any potential challenges that may arise during the process.
How long does it take for my residency status to change after submitting the form?
The time it takes for your residency status to change after submitting a Residency Declaration Form can vary widely depending on several factors, including the purpose of the declaration, the specific jurisdiction or institution involved, and their processing times. Here are some considerations:
- Purpose of the Declaration: The purpose for which you are declaring residency can impact the processing time. For example, if you are declaring residency for in-state tuition at a college or university, the institution may have specific deadlines and processing schedules tied to academic semesters.
- Jurisdiction: Different states or regions may have varying processing times and procedures for changing residency status. The processing time can depend on the efficiency of the government agency or institution responsible for reviewing and approving residency changes.
- Documentation: The time it takes to process your residency declaration may also depend on how quickly you provide all required documents and information. Delays in document submission can prolong the process.
- Notarization: If the Residency Declaration Form requires notarization, you’ll need to schedule an appointment with a notary public, which can add some additional time to the process.
- Review and Verification: Government agencies, educational institutions, or other authorities may need time to review and verify the information and documents you submitted. This can range from several weeks to several months.
- Appeals and Challenges: In cases where there are disputes or challenges to your residency declaration, the process can be further delayed as legal or administrative proceedings take place.
- Specific Deadlines: If your declaration has a specific deadline tied to an event, such as a school semester, it’s crucial to submit the form well in advance to ensure your residency status is updated in time.
To get a better idea of the expected processing time for your specific situation, it’s advisable to contact the relevant authority, institution, or government agency responsible for handling residency declarations. They can provide you with information on typical processing times and any specific deadlines you need to meet.
In general, it’s wise to submit your Residency Declaration Form as early as possible, especially if it’s tied to important events like school enrollment or tax filing, to allow ample time for processing and avoid potential issues.
Can I appeal a decision made based on my Residency Declaration Form?
Yes, you can typically appeal a decision made based on your Residency Declaration Form if you believe the decision is incorrect or unjust. The appeal process can vary depending on the jurisdiction, institution, or authority responsible for handling residency declarations, but here are some general steps to consider:
- Review the Decision: Start by carefully reviewing the decision letter or communication you received. Understand the reasons for the denial or unfavorable decision.
- Check Appeal Guidelines: Consult the guidelines and instructions provided by the relevant authority or institution regarding the appeal process. These guidelines will outline the procedures, deadlines, and requirements for filing an appeal.
- Gather Additional Documentation: If the denial was due to missing or insufficient documentation, gather any additional required documents or evidence that can support your case during the appeal.
- Prepare a Written Appeal: Write a formal written appeal letter. In the letter, explain the reasons you believe the decision was incorrect and provide any supporting evidence. Be clear and concise in your communication.
- Follow Appeal Procedures: Submit the appeal letter and any required documents following the specified procedures and within the designated timeline. Ensure that you address the appeal to the appropriate office or individual.
- Request a Hearing (if applicable): Some appeals may involve a hearing where you can present your case in person. If this option is available, consider requesting a hearing and preparing your arguments accordingly.
- Legal Counsel: If your case is complex or involves significant legal issues, you may want to consult with an attorney who specializes in residency or immigration law. They can provide legal guidance and representation during the appeal process.
- Track the Appeal: Keep a record of all correspondence related to the appeal, including dates, times, and names of individuals you communicate with. This documentation can be valuable if you need to escalate the appeal.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the progress of your appeal. If the appeal process is taking longer than expected, follow up with the relevant authority for updates.
- Accept the Decision or Escalate: After the appeal is reviewed, you will receive a final decision. If the decision is in your favor, your residency status will be updated accordingly. If the decision remains unfavorable, you may have the option to escalate the matter further, such as through a higher-level appeal or legal action.
Remember that the specific appeal process and requirements can vary widely depending on your location and the nature of your residency declaration. It’s essential to carefully follow the provided guidelines and seek legal advice if necessary to ensure your rights are protected throughout the appeal process. Our Affidavit Form is also worth a look at
Are Residency Declaration Forms required for all types of residency applications?
Residency Declaration Forms are not universally required for all types of residency applications. Whether or not you need to submit a Residency Declaration Form depends on the specific purpose and requirements of your residency application, as well as the policies of the relevant jurisdiction or institution. Here are some common scenarios where Residency Declaration Forms may or may not be required:
- In-State Tuition Eligibility: Many colleges and universities require students to submit Residency Declaration Forms to establish eligibility for in-state tuition rates. These forms typically include information about your residency status, domicile, and supporting documentation.
- Voter Registration: When registering to vote in a new state or jurisdiction, you may be required to complete a Residency Declaration Form or provide proof of residency as part of the voter registration process.
- State Income Tax Purposes: Some states require individuals to declare their residency status on state income tax returns. While this may not involve a specific Residency Declaration Form, you may need to provide information about your residency.
- Driver’s License or ID Card: When applying for a driver’s license or state identification card, you may need to provide proof of residency. While not a traditional Residency Declaration Form, this application process is related to residency documentation.
- Immigration and Visa Applications: Residency requirements and documentation can vary significantly for immigration and visa applications. While Residency Declaration Forms may not be used in these cases, applicants may need to provide extensive documentation related to their intended residency.
- Employment Verification: Employers may request proof of residency or legal authorization to work in a specific jurisdiction as part of the employment verification process.
- Public Assistance or Benefits: Applicants for public assistance or government benefits may need to provide documentation related to their residency and eligibility.
- Property Ownership and Taxes: Property owners may need to declare their residency for property tax purposes, and documentation may be required.
It’s essential to carefully review the requirements of your specific residency application to determine whether a Residency Declaration Form or other supporting documentation is necessary. Contacting the relevant authority or institution and seeking guidance can help ensure that you provide the correct documentation and complete the application accurately. In addition, you should review our Citizenship Affidavit form.
How to Create a Residency Declaration Form?
Creating a Residency Declaration Form involves careful consideration of the purpose and requirements of the form. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you create a Residency Declaration Form:
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope
- Determine the specific purpose of the Residency Declaration Form. Is it for in-state tuition eligibility, voter registration, tax purposes, or another reason?
- Define the scope of the form by outlining the information you need from the declarant to establish residency.
Step 2: Research Legal Requirements
- Research the legal requirements and regulations related to residency declarations in your jurisdiction. Ensure compliance with local, state, or federal laws.
- Identify any specific documents or information that must be included on the form.
Step 3: Create a Header
- Create a header for the form, including the title “Residency Declaration Form,” the name of the jurisdiction or institution, and the date of the form.
Step 4: Provide Instructions
- Include clear and concise instructions at the beginning of the form. Explain the purpose of the form, who should complete it, and any supporting documentation required.
Step 5: Personal Information Section
- Create a section for the declarant’s personal information, including:
- Full legal name
- Date of birth
- Contact information (address, phone number, email)
- Social security number or other identification details (if required)
Step 6: Residency Information Section
- Design a section where the declarant can provide information related to their residency, such as:
- Current address (where they claim residency)
- Date of establishing residency
- Previous address (if applicable)
- Domicile information (if relevant)
Step 7: Supporting Documentation
- Specify a section for attaching supporting documentation. Clearly list the types of documents required, such as utility bills, lease agreements, or voter registration cards. Include a checklist for easy reference.
Step 8: Legal Declarations and Signature
- Include a section where the declarant must legally affirm the information provided. This section typically includes statements like:
- “I declare that the information provided is true and accurate to the best of my knowledge.”
- “I understand that false statements may have legal consequences.”
Step 9: Signature and Date
- Create space for the declarant’s signature and date. Some forms may require notarization or the presence of a witness. Specify these requirements if necessary.
Step 10: Contact Information
- Provide contact information for inquiries or assistance. Include the name, phone number, and email address of the relevant office or authority.
Step 11: Review and Testing
- Review the draft form for accuracy, clarity, and completeness. Ensure that it aligns with legal requirements.
- Test the form with a sample user to identify any usability issues or confusion.
Step 12: Finalize and Distribute
- Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and testing.
- Finalize the form and publish it through the appropriate channels, such as on a government website, at educational institutions, or at voter registration offices.
Step 13: Periodic Updates
- Periodically review and update the form to ensure it remains current and compliant with any changes in regulations or laws.
Remember that the specific content and format of the Residency Declaration Form can vary depending on its intended use and jurisdiction. Therefore, it’s crucial to tailor the facility form to meet the specific requirements of your situation while adhering to legal standards. Legal counsel or guidance from relevant authorities can be valuable during the creation process.
Tips for creating an Effective Residency Declaration Form
Creating an effective Residency Declaration Form is crucial to ensure accurate and legally compliant declarations. Here are some tips to help you design an effective form:
- Clarity of Purpose: Clearly define the purpose of the form at the beginning to help declarants understand why they need to complete it.
- Simple Language: Use plain and straightforward language. Avoid complex legal jargon that may confuse declarants.
- Clear Instructions: Provide step-by-step instructions on how to complete the form, including what information to provide and which documents to attach.
- Checklist: Include a checklist of required supporting documents to help declarants gather the necessary paperwork.
- Fields for All Relevant Information: Ensure that the form includes fields for all information needed to establish residency, such as current and previous addresses, dates of residency, and domicile details.
- Document Upload: If possible, create a digital version of the form that allows declarants to upload scanned copies of supporting documents for online submissions.
- Notary or Witness Section: If notarization or witnessing is required, clearly indicate where and how this should be done on the form.
- Contact Information: Include contact details for the relevant office or authority in case declarants have questions or need assistance.
- Legal Declarations: Include statements that declarants must sign to affirm the accuracy of the information provided and acknowledge the consequences of false statements.
- Privacy and Data Protection: Include a brief statement about how the collected information will be used and protected, ensuring compliance with data privacy laws.
- Version Control: Ensure that the form includes a version or revision date so that declarants can verify they are using the most up-to-date form.
- Usability Testing: Test the form with a diverse group of users to identify any issues with clarity, accessibility, or user-friendliness.
- Online Accessibility: If applicable, make the form available online and accessible through various devices and browsers to accommodate declarants’ preferences.
- Language Options: If your jurisdiction or institution serves a linguistically diverse population, consider offering the form in multiple languages.
- Regular Review: Periodically review and update the form to align with any changes in regulations or legal requirements.
- Education and Outreach: Accompany the form with educational materials or outreach efforts to help declarants understand the residency declaration process better.
- Legal Consultation: Seek legal counsel to ensure that the form complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
By following these tips, you can create an effective Residency Declaration Form that is user-friendly, legally sound, and helps declarants accurately establish their residency status for various purposes, from in-state tuition to voter registration.
In summary, a Residency Declaration Form serves as a vital tool for individuals to assert their residency status for various purposes, such as in-state tuition or voter registration. Its creation demands careful attention to legal requirements, clear instructions, and user-friendliness. By adhering to best practices and guidelines, an effective Residency Declaration Form empowers declarants to provide accurate information while complying with regulatory standards, facilitating smoother processes for all involved parties. You may also be interested in our Student Affidavit Forms.
Related Posts Here
-
Restaurant Schedule Form
-
Mobile Home Bill of Sale
-
Landlord Consent Form
-
60-Day Notice to Vacate Form
-
Financial Statement Form
-
Product Evaluation Form
-
Construction Contract
-
School Receipt Form
-
Restaurant Training Form
-
Daily Cash Log
-
Volleyball Evaluation Form
-
Holding Deposit Agreement Form
-
License Agreement Short Form
-
Fund Transfer Form
-
Business Financial Statement Form