Empower your real estate decisions with our definitive guide on Property Power of Attorney Forms. Tailored for property owners and investors, this guide illuminates how to effectively use, draft, and execute these forms. Packed with practical tips and legal insights, our resource simplifies complex processes, ensuring your property affairs are managed accurately and efficiently. Whether for buying, selling, or managing real estate, our guide is the key to navigating property power of attorney with confidence and precision.
What is the Property Power of Attorney Form?
A Property Power of Attorney Form is a legal document that allows an individual (the principal) to appoint someone else (the agent or attorney-in-fact) to manage their property affairs. This form gives the agent authority to handle tasks such as buying, selling, maintaining, or renting out property on behalf of the principal. It’s used when the principal cannot manage their property matters personally due to absence, illness, or other reasons.
What is the best Sample Property Power of Attorney Form?
Free 10+ Property Power of Attorney Forms
1. Property Power of Attorney Form Template

2. Durable Property Power of Attorney Form

3. Simple Property Power of Attorney Form

4. Blank Property Power of Attorney Form
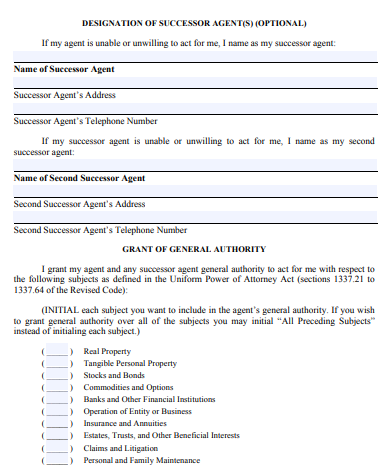
5. General Property Power of Attorney Form
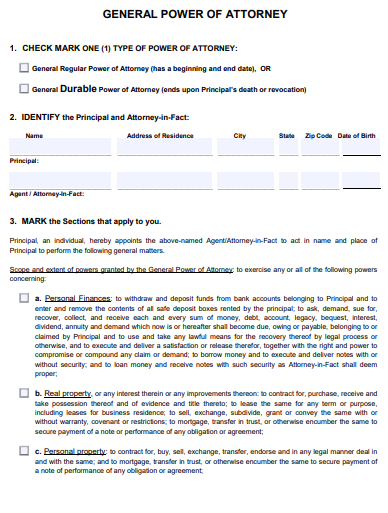
6. Arkansas Property Power of Attorney Form

7. Sample Property Power of Attorney Form
8. Unclaimed Property Power of Attorney Form

9. California Real Estate Power of Attorney Form

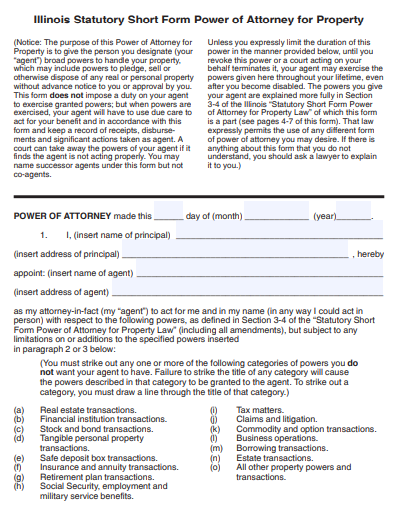
10. Illinois Property Power of Attorney Form

11. Special Property Power of Attorney Form

How do I write a Power of Attorney for my property?
Writing a Power of Attorney (POA) for your property involves several key steps to ensure it is legally sound and accurately reflects your intentions:
- Identify the Type of POA: Decide if you need a general POA, which covers a wide range of actions, or a specific POA, limited to certain property-related tasks.
- Select an Agent: Choose a trusted individual who will act as your agent or attorney-in-fact. This person should be reliable, competent, and preferably have some knowledge of managing property.
- Define the Powers: Clearly specify what property-related powers you are granting to your agent. This can include buying, selling, managing, leasing property, handling mortgage details, dealing with taxes, etc.
- Draft the Document: Write the POA document. Start with your full name and address, followed by the agent’s full name and address. Then list the specific powers granted.
- Add Duration: Specify when the POA will take effect and its duration. It can be for a fixed period, until a specific event occurs, or until you revoke it.
- Legal Requirements: Ensure the POA meets all legal requirements in your jurisdiction, which may include specific language or clauses.
- Include Revocation Clause: Mention how and when you can revoke the POA.
- Witnesses and Notarization: Depending on your state laws, you may need to sign the POA in front of witnesses and/or get it notarized.
- Sign and Date the Document: Both you and the agent should sign and date the document in the presence of a notary or witnesses, as required.
- Store Safely: Keep the original document in a secure place and provide copies to your agent and relevant parties, such as banks or real estate agents.
- Legal Consultation: It’s advisable to consult with an attorney to ensure the POA is valid, especially if it involves significant property matters or complex legal issues.
Writing a POA for your property is a serious undertaking that requires precision and legal knowledge to ensure it effectively represents your interests and is compliant with the law.
What is the validity of a power of attorney?
The validity of a Power of Attorney (POA) can vary depending on several factors:
- Duration Specified in the Document: Many POAs specify a start and end date. The POA is valid within this timeframe.
- Type of POA: A Durable Power of Attorney remains valid if the principal becomes incapacitated, whereas a Non-Durable POA becomes invalid upon the principal’s incapacitation.
- State Laws: Different states may have varying laws that affect the validity of a POA. For instance, some states require notarization or specific witnessing for the document to be legally valid.
- Completion of Purpose: If the POA is for a specific task, it becomes invalid once the task is completed.
- Revocation by the Principal: The principal can revoke the POA at any time, as long as they are mentally competent, which would immediately end its validity.
- Death of the Principal: A POA becomes invalid upon the death of the principal.
Understanding these factors is crucial to determine the validity of a specific Power of Attorney, as they can significantly impact how and when a POA is applied.
Can land be sold by power of attorney?
Yes, land can be sold by Power of Attorney (POA), provided the POA explicitly grants the agent the authority to conduct real estate transactions on behalf of the principal. Here are key points to consider:
- Specific Authority: The POA must clearly state that the agent has the power to sell property, including specific details about the land in question, if applicable.
- Compliance with Law: The sale must comply with all relevant state laws, which may include requirements for the POA to be recorded or registered.
- Valid Execution: The POA should be properly executed, often requiring notarization, and sometimes witnesses, to be legally valid for selling property.
- Agent’s Duties: The agent is bound to act in the principal’s best interest, which includes obtaining a fair price and handling the transaction legally and ethically.
- Revocation: If the principal revokes the POA or becomes incapacitated (if the POA is not durable), the agent can no longer legally sell the land.
- Acceptance by Third Parties: Some buyers and title companies may have specific requirements or hesitations in dealing with an agent under a POA. It’s important to ensure all parties are informed and agreeable to the terms.
Before proceeding with the sale of land through a POA, it’s advisable to consult with a legal professional to ensure compliance with all legal requirements and proper execution of the sale.
What documents are required for power of attorney?
Is it safe to buy property on power of attorney?
Buying property through a Power of Attorney (POA) can be safe, but it requires careful consideration and due diligence. Here are some factors to ensure safety and legality in such transactions:
- Verify the POA: Ensure the POA is valid, legally binding, and specifically authorizes the sale of the property. Check if it has been properly executed, notarized, and, if necessary, registered.
- Confirm the Agent’s Authority: Make sure the agent (the person selling the property on behalf of the principal) has the explicit authority to sell the property as per the POA.
- Assess the Principal’s Consent: Confirm that the principal (the owner of the property) is aware of and consents to the sale. Be cautious if the principal is incapacitated.
- Legal and Title Checks: Conduct a thorough title search and legal checks on the property to ensure there are no encumbrances, liens, or legal disputes.
- Consult a Real Estate Attorney: Before proceeding, consult with a real estate attorney to verify the legality of the POA and the property transaction.
- Review State Laws: Different states have varying laws regarding property sales through POA. Ensure that all legal requirements are met.
- Transaction Transparency: Ensure that all aspects of the transaction, including price and terms, are transparent and in line with market practices.
- Written Agreement: Have a written sale agreement that clearly outlines all the terms and conditions of the sale.
- Principal’s Revocation Rights: Be aware that a POA can be revoked by the principal at any time, which could affect the transaction.
- Insurance and Protection: Consider title insurance to protect against any legal issues that might arise after the sale.
While buying property through a POA is common and can be safe, it’s crucial to proceed with caution and seek professional advice to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transaction.
How Power of Attorney of Property Is Applied in Practice
In practice, a Power of Attorney (POA) for property is applied in several ways to manage or transact on real estate on behalf of the principal (the person who grants the power). Here’s how it typically works:
- Execution of Legal Documents: The agent, under POA, can sign legal documents related to property transactions. This includes deeds, mortgages, leases, and other real estate documents.
- Buying or Selling Property: The agent can buy or sell property on behalf of the principal. This involves negotiating terms, executing purchase agreements, and handling closings.
- Managing Property: For rental properties, the agent can manage day-to-day operations, including collecting rent, paying property-related bills, and handling maintenance and repairs.
- Mortgage and Refinancing Transactions: The agent can manage mortgage-related tasks, including refinancing or taking out a mortgage on the principal’s property.
- Legal Representation: The agent may represent the principal in legal matters related to the property, such as disputes, evictions, or legal negotiations.
- Tax Matters: Handling property taxes and other tax-related issues associated with the property can also be a part of the agent’s responsibilities.
- Compliance with Laws: The agent must ensure all transactions and management practices comply with relevant laws and regulations.
- Acting in Principal’s Interest: The agent is legally obligated to act in the best interest of the principal, making decisions that align with the principal’s wishes and best interests.
- Limitations and Restrictions: The specific powers and limitations are detailed in the POA document. The agent can only perform actions within the scope granted by the POA.
- Record Keeping: The agent should maintain records of all transactions and decisions made concerning the property.
In practice, a POA for property is a powerful tool for managing real estate, especially when the principal is unable to do so themselves. It’s crucial for the agent to understand their responsibilities and act in a fiduciary capacity, maintaining transparency and accountability in all actions taken on behalf of the principal.
How to Prepare a Property Power of Attorney Form
Preparing a Property Power of Attorney (POA) Form involves several steps to ensure its legality and effectiveness:
Step 1: Determine the Scope
- Decide the specific powers related to property management or transactions you want to grant. This could include buying, selling, maintaining, or leasing property.
Step 2: Select Your Agent
- Choose a trustworthy and capable individual to act as your agent. This person should have a good understanding of property management and real estate transactions.
Step 3: Draft the POA Form
- You can use a standard form or draft a customized document. The form should include:
- Your full name and address (Principal).
- The agent’s full name and address.
- A detailed description of the property-related powers granted.
- Any restrictions or limitations on these powers.
Step 4: Include Duration
- Specify the duration for which the POA is effective. It can be for a defined period or until a certain event occurs, like the sale of a property.
Step 5: Legal Formalities
- Make sure your POA form complies with the legal requirements of your state, such as notarization and witnessing.
Step 6: Sign and Date the Form
- Both you and your agent need to sign and date the form. The signing might need to be done in the presence of a notary public and possibly witnesses, depending on your state laws.
Step 7: Notarize the Document
- Getting the document notarized adds a layer of legal validity.
Step 8: Witnesses
- If required by your state, have one or more adult witnesses sign the document.
Step 9: Distribute Copies
- Provide a copy of the signed and notarized document to your agent and any third parties, like banks or real estate agents, who will interact with the agent.
Step 10: Safe Storage
- Keep the original document in a secure place. Inform family members or other important contacts where it can be found, if necessary.
Step 11: Legal Consultation
- It’s recommended to consult with a lawyer, especially for more complex property matters, to ensure that the POA meets all legal requirements and your specific needs.
By following these steps, you can create a Property Power of Attorney that is legally sound and tailored to your specific requirements.
Tips for Using Effective Property Power of Attorney Form
Using a Property Power of Attorney (POA) effectively requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some tips to ensure its effectiveness:
- Specify the Powers Clearly: Define the specific property-related tasks you are authorizing. This could include buying, selling, managing, or leasing property. Avoid vague language to prevent misunderstandings.
- Choose a Trustworthy Agent: Select someone who is reliable and understands property matters. This person should be capable of making informed decisions about your property.
- Understand the Legal Implications: Be aware of the legal responsibilities and powers you are granting to the agent. Ensure they align with your intentions.
- Comply with State Laws: Different states have varying requirements for legal validity, including notarization and witnesses. Make sure your POA complies with these laws.
- Define Duration: Clearly state when the POA will take effect and when it will expire. Some POAs are set for a specific time frame, while others are tied to the completion of a certain task.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review the POA to ensure it still meets your needs and reflects any changes in your situation or property holdings.
- Keep Accurate Records: Ensure that both you and your agent keep detailed records of all transactions and decisions made regarding the property.
- Communicate with Your Agent: Maintain open lines of communication with your agent. Discuss your expectations, and provide guidance on how you want your property to be managed.
- Secure Storage: Store the original POA document in a safe place and provide copies to relevant parties, such as banks or real estate agents.
- Plan for Revocation: Understand the process for revoking the POA, should the need arise. This usually requires a written notice.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting with a real estate attorney or legal expert, especially for complex property transactions or if the POA involves significant assets.
By following these tips, you can use a Property Power of Attorney form effectively, ensuring that your property affairs are handled according to your wishes and in compliance with legal standards.
What Are the Rights of Power of Attorney in Property?
The rights of a Power of Attorney in property include managing, selling, leasing, and handling all legal matters related to the property as specified.
Can We Sell Property Through Power of Attorney?
Yes, property can be sold through a Power of Attorney if it explicitly grants the agent the authority to conduct such transactions.
How Many Days Is a Power of Attorney Valid?
The validity of a Power of Attorney can vary – it may be set for a specific period, till a task is completed, or until revoked.
Can Power of Attorney Holder Sell Property to His Wife?
A Power of Attorney holder can sell property to his wife if the POA allows such transactions and there’s no conflict of interest or legal impediment.
Can Power of Attorney Be Cancelled?
Yes, a Power of Attorney can be cancelled or revoked by the principal at any time, as long as they are mentally competent.
A Property Power of Attorney Form is a crucial legal tool for delegating property management and transactions. Following this guide ensures effective creation and usage, from selecting a reliable agent to understanding legal compliance. With clear guidelines and practical tips, this form enables efficient handling of property matters, providing peace of mind and ensuring decisions align with your specific needs and intentions.
Related Posts
-
10+ Free New Hampshire (NH) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nevada (NV) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nebraska (NE) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Montana (MT) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Missouri (MO) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Minnesota (MN) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Mississippi (MS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Massachusetts (MA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maryland (MD) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maine (ME) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Louisiana (LA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kentucky (KY) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kansas (KS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Iowa (IA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Indiana (IN) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
