Discover the key to effective legal management with our comprehensive guide on Minnesota Power of Attorney (POA) Forms. This essential resource provides valuable insights on utilizing POA forms, ensuring your decisions are legally sound and representative of your wishes. Whether for financial, health, or personal matters, our tips and how-to’s cater to all needs. Empower yourself with knowledge about Minnesota’s POA requirements, safeguarding your interests and simplifying complex legal processes with confidence.
What is the Minnesota Power of Attorney Form?
The Minnesota Power of Attorney Form is a legal document that allows you to appoint someone to make decisions on your behalf. This person, known as an agent or attorney-in-fact, can manage your financial, health, or other personal matters if you’re unable to do so. The form specifies what powers your agent has, ensuring they act according to your wishes. It’s a key tool for planning and managing your affairs in Minnesota.
What is the Best Sample Minnesota Power of Attorney Form?
Creating a sample Minnesota Power of Attorney form with fillable blanks involves designing a template that covers essential elements while leaving key details to be filled in by the user. Here is a simplified version:
MINNESOTA POWER OF ATTORNEY FORM
Principal’s Information:
- Name: [_____________________________]
- Address: [_____________________________]
- Phone: [_____________________________]
Agent’s Information:
- Name: [_____________________________]
- Address: [_____________________________]
- Phone: [_____________________________]
Type of Power of Attorney:
- General Power of Attorney
- Limited Power of Attorney
- Durable Power of Attorney
- Medical Power of Attorney
Powers Granted (specify if Limited POA):
- Financial Decisions
- Real Estate Management
- Medical Decisions
- Personal Affairs
- Other: [_____________________________]
Duration of Power of Attorney:
- Effective Date: [//______]
- Termination Date (if applicable): [//______]
Special Instructions:
- [______________________________________]
Signatures:
- Principal’s Signature: [______] Date: [//]
- Agent’s Signature: [______] Date: [//]
Witnesses (if required):
- Witness #1 Name: [_____________________________]
- Signature: [______] Date: [//]
- Witness #2 Name: [_____________________________]
- Signature: [______] Date: [//]
Notary Acknowledgment (if required):
- State of Minnesota, County of [__________________]
- Notary Public Signature: [____________________]
- Date: [//______]
- My Commission Expires: [____________________]
[NOTICE: This form is a sample and should be customized to fit individual circumstances. Consultation with a legal professional is advised to ensure compliance with state laws and regulations.]
This template is a basic framework and should be tailored to fit specific requirements and legal standards. For an official and legally binding document, it’s important to consult with a legal professional.
1. State of Minnesota Power of Attorney Form

2. Minnesota Statutory Short Power of Attorney Form

3. Minnesota Sample Power of Attorney Form

4. Minnesota Power of Attorney Form
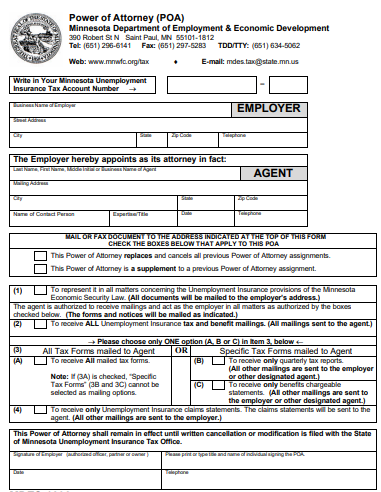
5. Minnesota Minor Child Power of Attorney Form

6. Minnesota Medical Power of Attorney Form

7. Minnesota Limited Power of Attorney Form

8. Minnesota Individual Power of Attorney Form
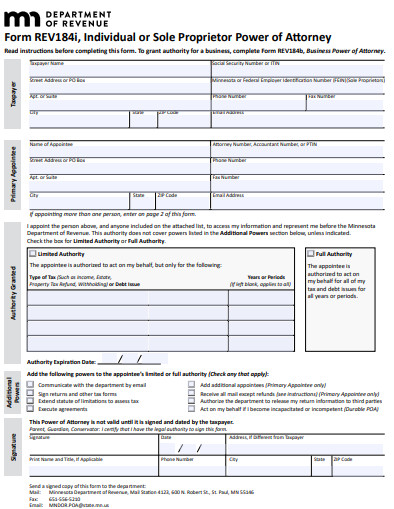
9. Minnesota Healthcare Power of Attorney Form
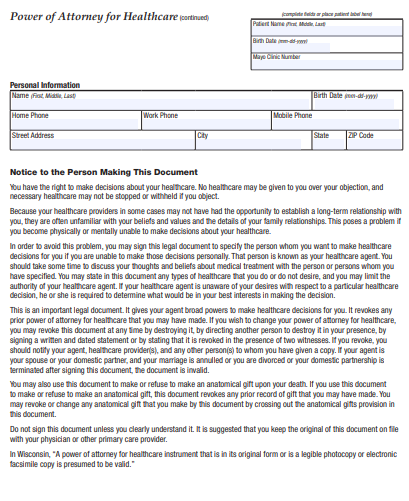
10. Minnesota General Power of Attorney Form
11. Minnesota General Power of Attorney Form

Does a Power of Attorney Need to be Notarized in Minnesota?
In Minnesota, notarizing a Power of Attorney (POA) form is essential for legality. This process validates the document, ensuring it’s recognized in legal and financial institutions. Notarization prevents fraud, confirming the principal’s identity and their voluntary decision. For a Minnesota POA to be effective, involving a notary public is a critical step, adding an extra layer of legal authenticity and recognition.
Examples of Notarization in POA Forms:
- Financial POA: Requires notarization for transactions involving banks or real estate.
- Healthcare POA: Notarization ensures medical directives are respected.
- General POA: Notarizing a General POA adds credibility, especially for broad powers.
- Limited POA: Notarization in Limited POA is vital for specific transactions.
- Durable POA: Notarization is crucial to uphold the form’s validity even if the principal becomes incapacitated.
How Do I Get a Durable Power of Attorney in Minnesota?
Obtaining a Durable Power of Attorney (DPOA) in Minnesota involves selecting a trusted agent and clearly defining their powers. The DPOA remains effective even if you become incapacitated. It’s important to use a state-specific form, ensure all legal requirements are met, and ideally consult with a legal professional for guidance.
Examples of Durable POA Scenarios:
- Long-term Illness: Appointing an agent for financial decisions during illness.
- Elderly Care: Assigning a family member for elder care decisions.
- Business Management: Delegating business affairs during unavailability.
- Real Estate Management: Assigning an agent to handle property transactions.
- Investment Decisions: Authorizing an agent for investment management.
What is a Power of Attorney Form for Taxes in Minnesota?
A Power of Attorney form for taxes in Minnesota authorizes a designated individual to handle tax-related matters on your behalf. This includes filing taxes, accessing records, and making decisions about tax payments and disputes. It’s a key document for delegating tax responsibilities, ensuring your tax affairs are managed efficiently and in compliance with Minnesota tax laws.
Examples:
- Tax Filing Representation: Authorizes an agent to file state and federal taxes on your behalf.
- Tax Payment Arrangement: Enables the agent to set up payment plans for due taxes.
- Handling Tax Disputes: Empowers the agent to represent you in disputes with tax authorities.
- Accessing Tax Records: Allows the agent to access your tax records for accurate filing.
- Amending Tax Returns: Permits the agent to make necessary amendments to previously filed tax returns.
How Does Power of Attorney Work in MN?
Understanding Power of Attorney in Minnesota
A Power of Attorney (POA) in Minnesota authorizes a designated individual, known as the agent, to make decisions on behalf of another person, the principal. This legal document grants the agent authority to handle financial, legal, or health-related matters. Minnesota law requires POAs to be in writing, signed, and notarized. The scope of authority can be broad or limited, depending on the principal’s preferences.
Key Elements of Minnesota POA
In Minnesota, a POA must clearly identify both the principal and the agent, outlining the agent’s powers. It’s crucial to choose a trustworthy agent, as they will have significant control over the principal’s affairs. The document should also specify if the POA is durable, meaning it remains effective even if the principal becomes incapacitated.
POA for Health Care Decisions
Minnesota allows for a Health Care Directive, a type of POA focusing on medical decisions. This directive enables the agent to make healthcare decisions if the principal is unable to do so, ensuring their medical preferences are respected.
Financial Power of Attorney
A Financial POA in Minnesota grants the agent authority to manage the principal’s financial matters. This can include paying bills, managing investments, and handling property transactions. It’s a vital tool for estate planning and managing affairs in case of incapacity.
Revoking a Power of Attorney
In Minnesota, a POA can be revoked at any time by the principal, as long as they are mentally competent. This revocation must be in writing and follow specific legal procedures to be effective.
How Long is a Power of Attorney Good for in Minnesota?
Duration of a Minnesota POA
In Minnesota, the duration of a Power of Attorney depends on the type and terms specified in the document. Unless stated otherwise, a POA remains effective until the principal’s death or revocation.
Durable Power of Attorney
A Durable POA in Minnesota remains valid even if the principal becomes incapacitated. This type is often used for long-term planning, ensuring continuous management of the principal’s affairs.
Non-Durable POA
A Non-Durable POA is limited and ceases to be effective if the principal becomes incapacitated. It’s typically used for specific transactions or for a limited time period.
Springing Power of Attorney
A Springing POA becomes effective upon a specific event, usually the incapacity of the principal. It’s a way to ensure that the POA is only in use when absolutely necessary.
POA Termination Conditions
In Minnesota, a POA can terminate upon the principal’s death, revocation, or if the POA document specifies an end date. Additionally, if the appointed agent is unable to serve and no successor is named, the POA may also end.
What is a Medical Power of Attorney in Minnesota?
A Medical Power of Attorney in Minnesota is a legal document empowering a designated individual to make healthcare decisions on behalf of someone unable to do so. This authority includes choices about medical treatments, healthcare providers, and end-of-life care. It’s crucial for Minnesota residents to understand its significance for ensuring their medical wishes are respected, especially in critical health situations.
1. Designating a Health Care Agent
- In Minnesota, a Medical Power of Attorney allows you to appoint a trusted person as your health care agent. This agent makes medical decisions for you if you’re incapacitated. It’s vital to choose someone who understands your healthcare preferences and values.
2. Specifying Treatment Preferences
- This document lets you outline specific medical treatments you do or do not want. It ensures that your healthcare preferences are followed, particularly in situations where you cannot communicate your wishes.
3. Legal Recognition in Minnesota
- Minnesota law recognizes the authority of a Medical Power of Attorney, ensuring healthcare providers follow the decisions made by your appointed agent, aligning with your stated preferences.
4. End-of-Life Care Decisions
- A critical aspect of this document is specifying your wishes regarding end-of-life care. This can include instructions on life-sustaining treatments and palliative care, providing clarity and peace of mind for both you and your loved ones.
5. Revocation and Amendments
- In Minnesota, you have the right to revoke or amend your Medical Power of Attorney at any time, as long as you are mentally competent. This flexibility allows you to adjust your instructions as your health or personal circumstances change.
Who Has Power of Attorney After Death if There is No Will?
When someone passes away without a will, the concept of Power of Attorney After Death becomes a significant legal matter. Typically, Power of Attorney ceases upon death. The estate’s administration then falls under probate law, with a court-appointed executor or administrator handling the deceased’s affairs.
1. Role of Probate Court
- In the absence of a will, the probate court steps in to appoint an executor or administrator. This individual is responsible for managing and distributing the deceased’s assets according to state laws.
2. Intestate Succession Laws
- Intestate succession laws determine how assets are distributed when there is no will. These laws vary by state but generally prioritize spouses, children, and other close relatives.
3. Estate Administration Duties
- The appointed executor or administrator handles duties like paying debts, closing accounts, and distributing assets. They act in the best interest of the estate, adhering to legal and ethical standards.
4. Legal Representation
- In some cases, family members may seek legal representation to ensure fair and lawful handling of the estate. This can be crucial in complex situations or when disputes arise.
5. No Continuing Power of Attorney
- It’s important to understand that any Power of Attorney arrangement ends upon death. Post-death, the estate’s management is governed by probate law, not by the deceased’s previously designated attorney-in-fact.
How to Prepare a Minnesota Power of Attorney Form
Understanding the Basics of a Minnesota Power of Attorney
A Power of Attorney (POA) in Minnesota is a legal document that grants one person (the agent) the authority to act on behalf of another (the principal). This document is crucial for various situations, such as managing financial affairs, making healthcare decisions, or handling business transactions. It’s essential to understand the different types of POAs, including General, Limited, Durable, and Health Care POAs, each serving distinct purposes.
Step 1: Determine the Type of POA Needed
Firstly, identify the specific type of Power of Attorney required. A General POA offers broad powers to the agent, while a Limited POA restricts the agent to specific tasks or timeframes. A Durable POA remains in effect even if the principal becomes incapacitated, and a Health Care POA focuses on medical decisions.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Agent
Choosing a trustworthy and competent agent is critical. This person should be reliable, have a good understanding of your wishes, and be capable of making decisions under pressure. Consider factors like the agent’s proximity, financial acumen, and willingness to serve.
Step 3: Drafting the POA Document
While templates are available online, it’s advisable to consult with a legal professional to ensure the document meets all Minnesota legal requirements. The POA must clearly state the principal’s name, the agent’s name, and the powers granted. It should also specify the duration of the POA.
Step 4: Including Necessary Legal Terms
Incorporate key legal terms to ensure clarity and legal validity. Terms like “durable,” “revocation,” and “incapacity” should be defined and used appropriately. The document should also outline the conditions under which the POA will become effective or terminate.
Step 5: Signing and Notarization
In Minnesota, the POA must be signed by the principal in the presence of a notary public. This step is crucial for the document’s legality. Ensure the signing process adheres to Minnesota state laws, including any witness requirements.
Step 6: Distributing Copies of the POA
After notarization, distribute copies of the POA to relevant parties, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and family members. Keep the original document in a safe but accessible place.
Step 7: Revoking or Amending the POA
Understand the process for revoking or amending the POA. The principal can revoke the POA at any time as long as they are mentally competent. Any revocation should be in writing and follow the same formalities as the original POA.
Step 8: Regular Review and Update
Regularly review and update the POA to reflect any changes in circumstances or wishes. This ensures that the document remains relevant and effective in fulfilling its intended purpose.
Creating a Minnesota Power of Attorney is a significant step in managing your affairs and ensuring your wishes are honored. By following these steps and consulting with legal professionals, you can create a comprehensive and legally sound POA tailored to your specific needs. Remember, effective communication and clarity are key in every step of this process.
Tips for Using Effective Minnesota Power of Attorney Form
Understanding the Minnesota Power of Attorney Form
A Power of Attorney (POA) in Minnesota grants an individual the authority to make decisions on behalf of another. It’s crucial to understand its scope, limitations, and the legal requirements in Minnesota. This form can cover financial, health, or general affairs, depending on the needs of the individual.
Selecting the Right Type of POA
Minnesota law recognizes several types of POAs, including General, Limited, Durable, and Health Care POA. Each serves different purposes:
- General POA allows broad powers.
- Limited POA is for specific transactions.
- Durable POA remains in effect even if the principal becomes incapacitated.
- Health Care POA focuses on medical decisions.
Identifying the Agent
Choosing a reliable and trustworthy agent is crucial. This person will have significant power over your affairs. Consider their ability to handle responsibilities and their understanding of your wishes.
Clearly Defining the Powers Granted
Be explicit about what powers the agent has. This clarity prevents misuse of the POA and ensures that the agent acts in your best interests. Specify limitations or special instructions if necessary.
Understanding the Legal Requirements
In Minnesota, POA forms must comply with state laws. This includes signature requirements and, in some cases, notarization. Ensure the form meets all legal standards to be valid.
Discussing with Family Members
Open communication with family members about the POA can prevent misunderstandings and conflicts. It’s important they understand your choices and the reasons behind them.
Reviewing and Updating Regularly
Circumstances change, and so should your POA. Regularly review and update it to reflect current wishes and situations. This might include changing the agent or adjusting the powers granted.
Consulting with a Legal Professional
While templates are available, consulting with a legal professional ensures that your POA is comprehensive, valid, and tailored to your needs. They can provide valuable advice and ensure legal compliance.
Safe Storage and Accessibility
Once completed, store the POA document in a safe but accessible place. Inform your agent and relevant parties of its location in case it needs to be accessed quickly.
Preparing for Incapacity
Consider a Durable POA to ensure that your affairs are managed if you become unable to make decisions. This foresight is crucial for seamless management of your affairs.
Avoiding Generic Forms
Generic forms might not meet specific Minnesota requirements. Tailoring your POA to Minnesota laws and your personal situation is essential for its effectiveness.
Understanding Revocation Process
Be aware of how and when you can revoke your POA. This knowledge empowers you to make changes as your situation evolves.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your Minnesota Power of Attorney form is effective, legally compliant, and truly represents your wishes. Remember, this document is a powerful tool for managing your affairs and should be treated with the utmost care and consideration.
Responsibilities of Power of Attorney in Minnesota
In Minnesota, a power of attorney’s responsibilities include managing financial, legal, and healthcare decisions as specified in the POA document, acting in the principal’s best interest.
Limitations of a Power of Attorney
A power of attorney’s limitations include inability to change the principal’s will, make decisions after the principal’s death, and act beyond granted powers or against the principal’s interests.
Recording a Power of Attorney in Minnesota
In Minnesota, recording a power of attorney is not mandatory unless it involves real estate transactions, where recording with the county is required for legal validity.
Having Multiple Powers of Attorney in Minnesota
Yes, in Minnesota, you can appoint multiple powers of attorney, either for different matters like healthcare and finances or as co-agents, provided it’s clearly outlined in the document.
Changing Power of Attorney in MN
To change a power of attorney in Minnesota, revoke the existing document in writing, notify the current agent, and create a new POA form reflecting the updated choices.
Understanding and effectively utilizing a Minnesota Power of Attorney form is crucial for managing your affairs. By selecting the right type, defining responsibilities, and adhering to legal requirements, you ensure your interests are safeguarded. Regular updates and professional advice further enhance its effectiveness, making it a vital tool for personal and financial management in Minnesota.
Related Posts
-
10+ Free New Hampshire (NH) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nevada (NV) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nebraska (NE) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Montana (MT) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Missouri (MO) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Mississippi (MS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Massachusetts (MA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maryland (MD) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maine (ME) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Louisiana (LA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kentucky (KY) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kansas (KS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Iowa (IA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Indiana (IN) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Illinois (IL) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips