A Credit Report Form is a key document for tracking financial transactions, showcasing credits and debits systematically. This guide delves into its importance, features, and uses. Whether for personal finance or business management, understanding a Credit Report Form ensures accuracy in financial record-keeping. With practical examples and tips, you’ll learn how to create a professional, comprehensive form that meets your needs. Accurate documentation not only improves financial transparency but also aids in compliance and planning.
Download Credit Debit Form Bundle
What is Credit Debit Form?
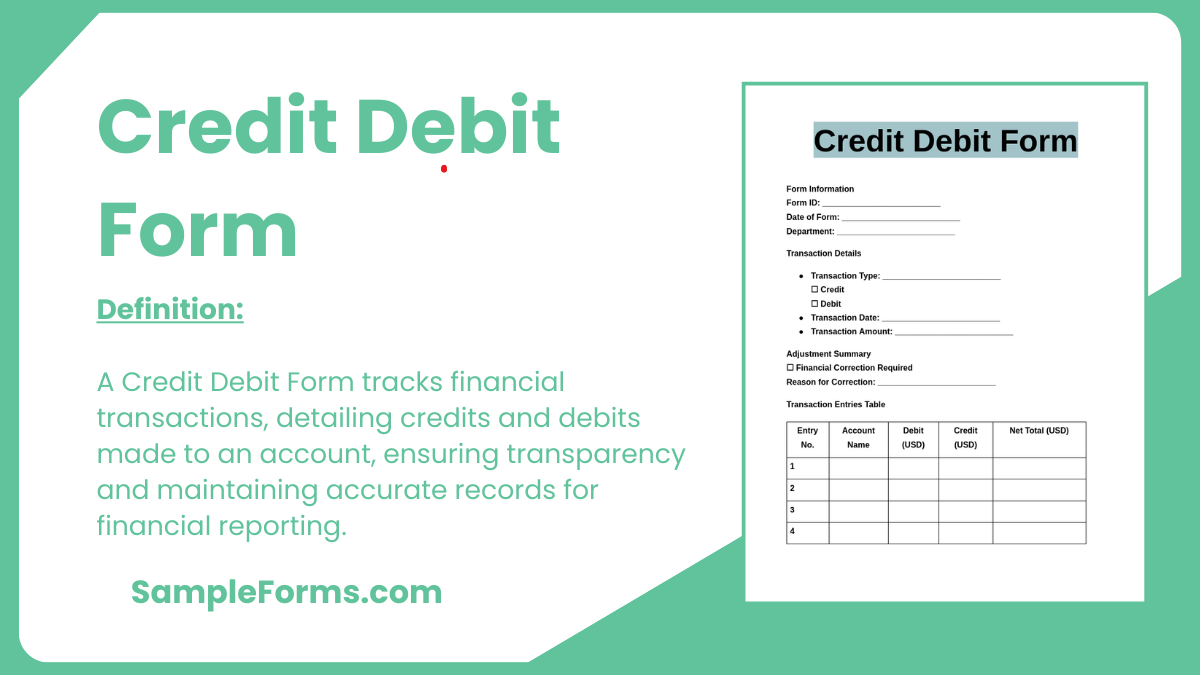
A Credit Debit Form is a financial document used to record transactions systematically. It tracks incoming credits and outgoing debits, providing a clear overview of account activity. This form ensures accurate financial monitoring, reconciliation, and transparency in both personal and professional settings. By organizing data, it simplifies budgeting, auditing, and reporting processes, making it an essential tool for effective financial management. Whether for business operations or individual use, a Credit Debit Form helps maintain control over financial records and facilitates smooth accounting practices.
Credit Debit Format
Account Holder Information
Full Name: __________________________
Account Number: __________________________
Bank Name: __________________________
Branch Address: __________________________
Transaction Details
Transaction Date: __________________________
Transaction Type (Credit/Debit): __________________________
Transaction Amount: __________________________
Transaction Reference Number: __________________________
Description/Purpose of Transaction: __________________________
Balance Information
Previous Balance: __________________________
New Balance: __________________________
Approval and Authorization
Name of Authorizer: __________________________
Designation: __________________________
Signature: __________________________
Date: __________________________
Credit Debit Worksheet Form

A Credit Debit Worksheet Form helps in organizing financial entries for analysis and reconciliation. Similar to a Business Credit Application Form, it simplifies record-keeping by detailing credits and debits for better financial clarity and control.
Asset Credit Debit Form

An Asset Credit Debit Form tracks asset transactions, including purchases, sales, and adjustments. Much like a Credit Card Authorization Form, it ensures accountability by recording precise financial details for effective asset management and reporting.
Financial Credit Debit Form

A Financial Credit Debit Form summarizes financial activities, offering insights into income and expenses. Comparable to a Credit Dispute Form, it ensures accuracy and aids in resolving discrepancies in financial records for businesses or individuals.
Bookkeeping Credit Debit Form PDF

A Bookkeeping Credit Debit Form PDF provides a ready-to-use template for documenting transactions. Like a Credit Application Form, it promotes consistency in financial documentation, ensuring transparent and efficient bookkeeping practices for any organization or individual.
Browse More Credit Debit Forms
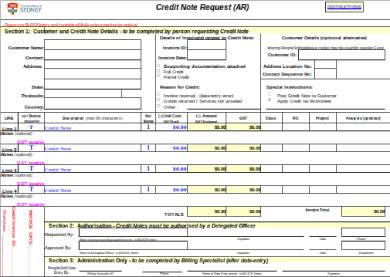
1. Debit Note Request Form
2. GST Debit Note Form
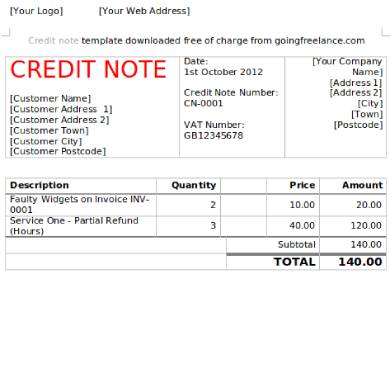
3. Credit Note Form Sample
4. Credit Note Request Form Sample
5. Credit Note Form Template
6. Credit Note Request Form
7. Bank Credit Inquiry Form
What is a debit and credit in layman’s terms?
Debits and credits represent transactions in accounting, showing how money moves in and out of accounts systematically. Key points include:
- Definition: A debit increases assets or expenses, while a credit increases liabilities or revenue in financial records.
- Purpose: They ensure balance in accounting, similar to how a Hotel Credit Card Authorization Form verifies payment details.
- Representation: Debits are recorded on the left, and credits are on the right side of a ledger.
- Application: Used in all financial activities, such as purchases, sales, or investments.
- Outcome: Proper use ensures accuracy and transparency in financial statements.
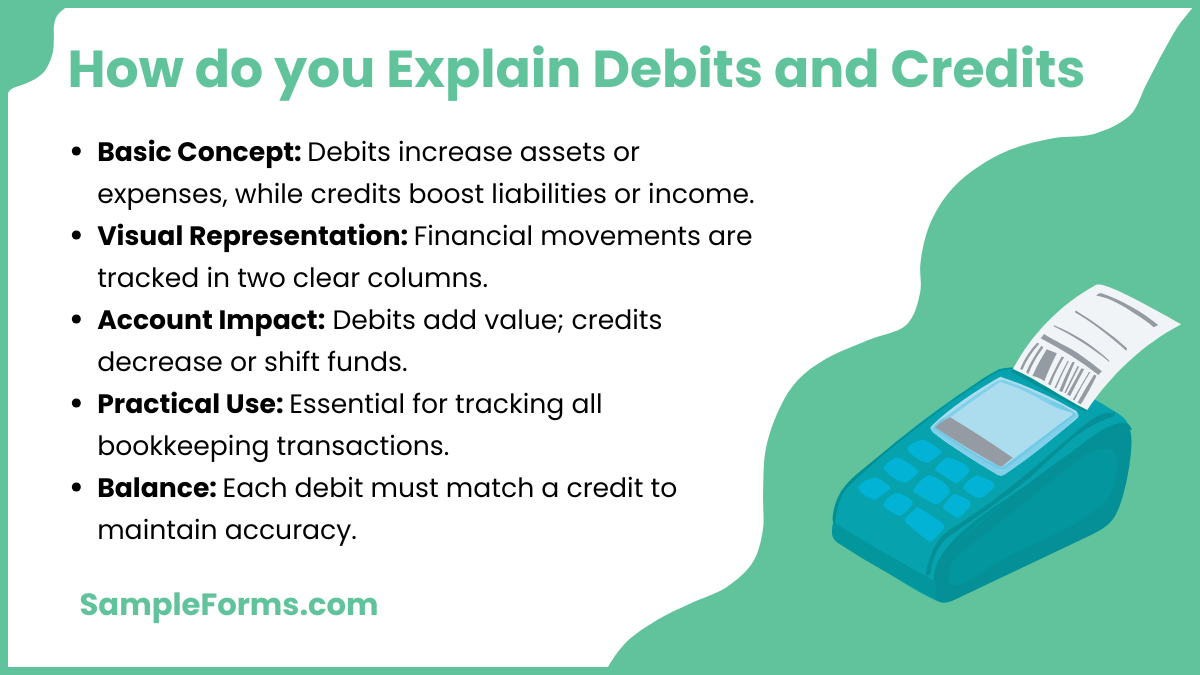
How do you explain debits and credits simply?
Debits and credits show financial activity within accounts, ensuring balance. Here’s how to explain them clearly:
- Basic Concept: Debits add value to assets or expenses, while credits subtract or increase liabilities and income.
- Visual Representation: Imagine a Business Credit Check Form listing financial movements in two columns for clarity.
- Account Impact: Debits increase an account’s positive value, while credits decrease or move funds elsewhere.
- Practical Use: These entries are vital for tracking every transaction in bookkeeping.
- Balance: Every debit entry must have a corresponding credit, maintaining equilibrium.
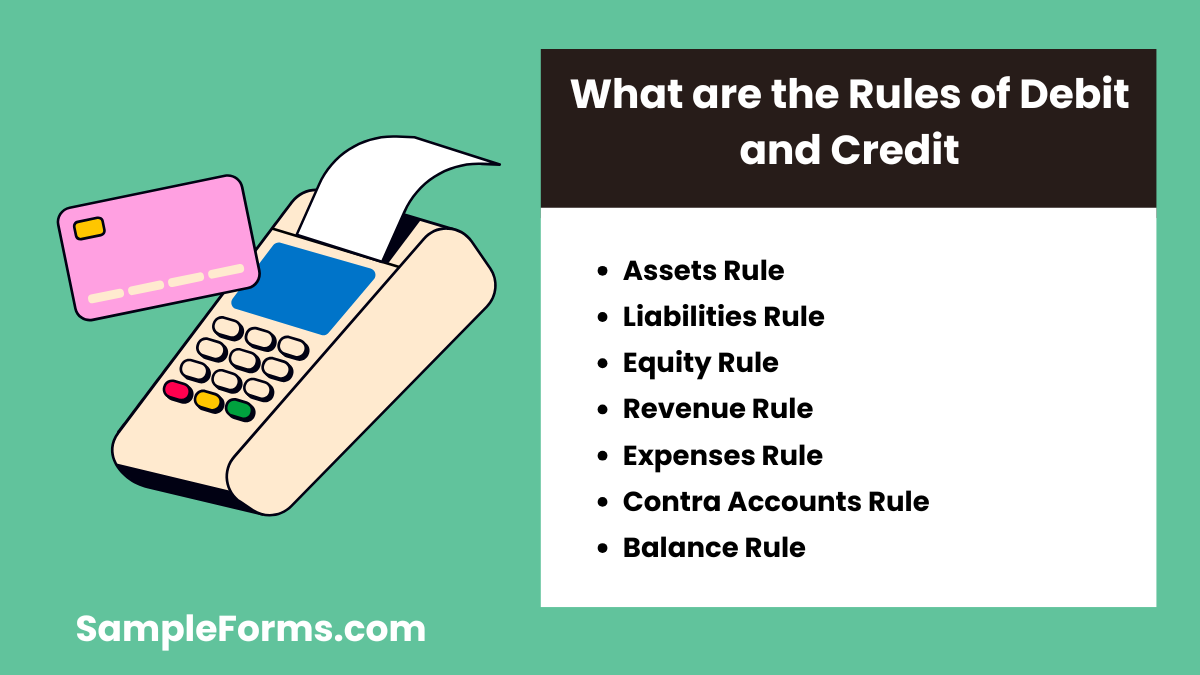
What are the rules of debit and credit?
The 7 rules ensure accurate financial recording by defining account behavior. Key rules include:
- Assets Rule: Debits increase assets, while credits decrease them, like maintaining a Credit Report Authorization Form.
- Liabilities Rule: Credits increase liabilities, and debits decrease them.
- Equity Rule: Credits add to equity, while debits reduce it.
- Revenue Rule: Credits increase revenue accounts, reflecting income growth.
- Expenses Rule: Debits increase expenses, tracking business costs.
- Contra Accounts Rule: Opposite rules apply for contra accounts, like accumulated depreciation.
- Balance Rule: Each transaction must balance debits and credits to ensure accuracy.
What are pearls in accounting?
“PEARLS” in accounting simplifies account classification for debits and credits. Each letter represents key concepts:
- P – Purchases: Recorded as debits, showing inventory additions or business expenses.
- E – Expenses: Tracked through debits, managing costs like a Business Credit Report aids in financial planning.
- A – Assets: Debits increase assets, essential for balance sheet accuracy.
- R – Revenue: Credits record revenue, ensuring growth visibility.
- L – Liabilities: Credits track obligations, including loans or payables.
- S – Stockholder’s Equity: Credits increase equity, reflecting company value.
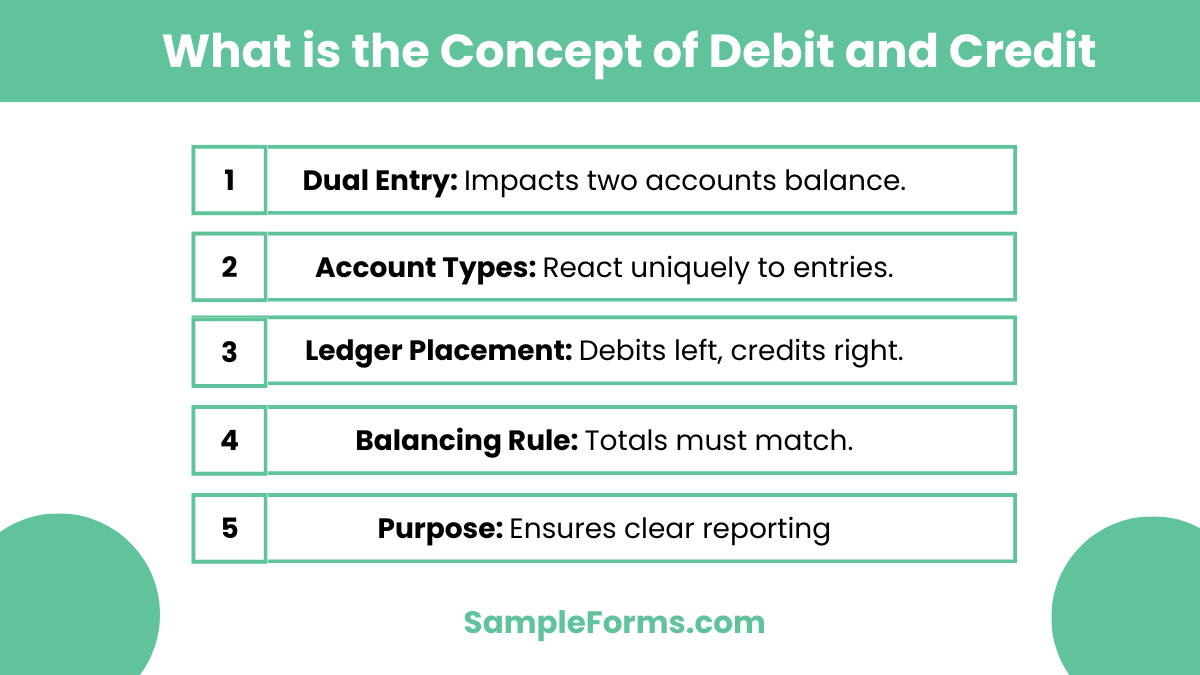
What is the concept of debit and credit?
Debits and credits form the core of double-entry accounting, ensuring balanced financial records. Key concepts include:
- Dual Entry: Every transaction impacts two accounts, ensuring equilibrium.
- Account Types: Different accounts, like assets or expenses, react differently to debits and credits.
- Ledger Placement: Debits on the left and credits on the right maintain organized records, akin to a Credit Inquiry Form.
- Balancing Rule: The total of debits must equal the total of credits for accuracy.
- Purpose: Facilitates clear financial analysis and reporting, crucial for businesses and individuals.
What is net debit and credit?
Net debit and credit refer to the total balance after accounting for all transactions. Like a Credit Authorization Form, it ensures accurate financial recording by balancing both sides effectively.
Is debit money in or out?
Debit represents money coming into an account, increasing assets or expenses. Similar to a Business Credit Checklist Form, it tracks cash inflows systematically for accurate record-keeping.
Is credit positive or negative?
Credit can be positive for liabilities or income and negative for assets. A Debit Order Form reflects its balance by documenting specific entries.
What is an example of credit debit?
An example is recording revenue as a credit and expenses as a debit in accounts, like creating a Financial Statement Form for tracking purposes.
What is a debit and credit for dummies?
Debits add to assets or expenses, while credits add to liabilities or income. Similar to a Financial Report Form, they maintain transaction clarity.
What is the easiest way to remember debits and credits?
Debits are left and credits are right in accounting. A Financial Questionnaire Form often serves as a structured guide for tracking them effectively.
Is credit money in or out?
Credit generally represents money going out, reducing assets or increasing liabilities, as outlined in a Financial Affidavit Form.
Which is better credit or debit?
Credit provides borrowing power, while debit deducts directly from your account. For business purposes, a Financial Evaluation Form can assess their suitability.
Are purchase returns a debit or credit?
Purchase returns are recorded as credits, reducing expenses. For clarity, a Business Financial Statement Form is used to track such transactions.
Is rent expense a debit or credit?
Rent expense is a debit entry as it increases expenses. Like a Financial Statement Form, it documents outgoing cash flows systematically.
A Credit Debit Form is a financial document used to record transactions systematically. It tracks incoming credits and outgoing debits, providing a clear overview of account activity. This form ensures accurate financial monitoring, reconciliation, and transparency in both personal and professional settings. By organizing data, it simplifies budgeting, auditing, and reporting processes, making it an essential tool for effective financial management. Whether for business operations or individual use, a Credit Debit Form helps maintain control over financial records and facilitates smooth accounting practices.
Related Posts
-
General Journal Form
-
FREE 5+ Gross Profit Margin Forms in Excel
-
FREE 5+ Petty Cash Register Samples in Excel | PDF
-
FREE 6+ Vendor Ledger Samples in PDF
-
Balance Sheet Form
-
Cash Receipt Journal Form
-
Accounts Receivable Ledger Form
-
FREE 4+ Financial Audit Forms in PDF
-
FREE 7+ Contemporary Sales Statement Samples in PDF
-
FREE 6+ Checkbook Register Forms in PDF | Excel
-
FREE 5+ Income Statement Spreadsheet Forms in PDF
-
Daily Cash Log
-
FREE 8+ Budget Transfer Forms in PDF | Excel
-
FREE 5+ Debenture Short Forms in PDF